As entrepreneurial culture takes off, it is providing people an alternative, more innovative, path to solve current problems. Moreover, entrepreneurship is contributing to development of regional needs, and solutions, research on advanced technologies and social development. Digital technologies, which are now becoming a major part of our lives, provide multi-faceted and fail-proof solutions to current struggles. Similarly, innovations in production technologies are allowing quick implementation of many diverse ideas. The positive impact small-scale-solutions is leading to the creation of micro-production laboratories. These labs, sometimes called “Makerspaces”, provide everyday access to advanced technologies. Collective working opportunities are bringing innovative groups, who previously had limited production opportunities in the past, to the global trade scene. At the same time, entrepreneurial culture created the right conditions for the birth of many new platforms focusing on equality, sociability and environmental responsibility which are now changing mass production trends.
Entrepreneurial Culture und Micro-Scale Fabrication
Problem-Solving Culture in Less Developed Countries
Today, advanced production is already a standard in some countries. Many other countries are now taking steps towards the future by investing into digital factories and micro-production laboratories. While digital factories support large-scale production and economic development, micro-production facilities increase local development.
Western countries who value entrepreneurial culture have heavily invested in establishing micro-production laboratories their cities. For this exact reason Western countries are now the leaders in advanced production research. On the other hand, developing countries have only just started invest in the establishment of similar laboratories. Countries that are investing in Makerspaces view these laboratories as a future source of income. Some of the most successful examples of makerspaces in developing countries, are in India, Philippines and Kenya. UN representatives expect these laboratories to serve an example for many future coworking spaces and local problem-solving hubs.
Cultivating a Problem-Solving Culture
Mumbai and Delhi-based Maker’s Asylum is a local FabLab establishedmission of introducing problem-solving culture. Maker’s Asylum observed the lack of problem-solving exercises in the local education system and set out change this. The lab also provides equal, accessible innovation environments and brings students, universities and organizations together to work on local problems in India. An example of such a problem can be battling poverty through research and development of tools. The makerspaces encourage project-based learning in its diverse set of members. Moreover, the the India-based laboratory does volunteer service with their members and portable laboratory. Currently Maker’s Asylum travels surrounding villages with their portable lab and organizes tech and science activities for village children. Their next goal is to become an open university where many innovative ideas are developed.

FabLab Mindanao, on the other hand, focuses on supporting national economy by bringing together Filipino students, small and medium-based companies. The laboratory in Mindanao meets the needs of small companies by developing customized solutions and increases the competitiveness of smaller companies in the global market. FabLab Mindanao not only provides entrepreneurs with technological opportunities and a working environment but also maintains a patent-based working system. The patent-system ensures continuous income to resident entrepreneurs while provides money to keep the laboratory economically independent. FabLab Mindanao’s the patent system “circular” economic strategy, one that will likely become very popular in the future.
Similar to the other examples, Gearbox is a MakerSpace based in Nairobi, Kenya. The fabrication lab’s main principle is to host science and design activities in the same environment. Gearbox welcomes entrepreneurs of all ages in its studios. The micro-production space contributes to the income of resident entrepreneurs by allowing them to teach technical production skills to interested locals and allowing them to host application-based workshops. Gearbox also has a small scale workshop program focusing on hands-on education approach, to introduce problem-solving based learning to Kenyans. At the same time, fabrication laboratory provides technological facilities and project rooms for entrepreneurs seeking solutions to problems in the city of Nairobi. Gearbox has already introduced a product called the Lumbrick Project to the Kenyan market. The Lumbrick project offers people an alternative energy source to coal made by recycling organic waste.

Influence of Advanced Technologies on Societies
The World Economic Forum highlighted the positive impacts of advanced production technologies and entrepreneurial culture can bring to societies. Forum representatives noted that the use of technologies such as 3D printing, advanced robotic manufacturing, data analysis, and smart manufacturing technique has potential to speed up the development of growing countries and vulnerable populations. In the same way forum members tied the development potential of technologies to increase in production efficiency, worker education level and decrease in cost of energy and materials.
United Nations stated that it will be possible to observe the positive socio-economic impacts of advanced production in developing countries, only if these countries are willing to increase their R&D investments. Representatives mentioned that investments towards advanced technologies increased from 1.4 trillion in 2010 to 2.2 trillion in 2020. On the other hand, UN members emphasized that current investments are not enough to design a new future. Representatives also mentioned that current investments were not enough to speed up the development pace of growing countries. Furthermore, UN representatives stated that investors should support small industries in underdeveloped countries as much as small industries in developed countries. They illustrated thier point by noting that only 35% of small industries have access to money for investment purposes.
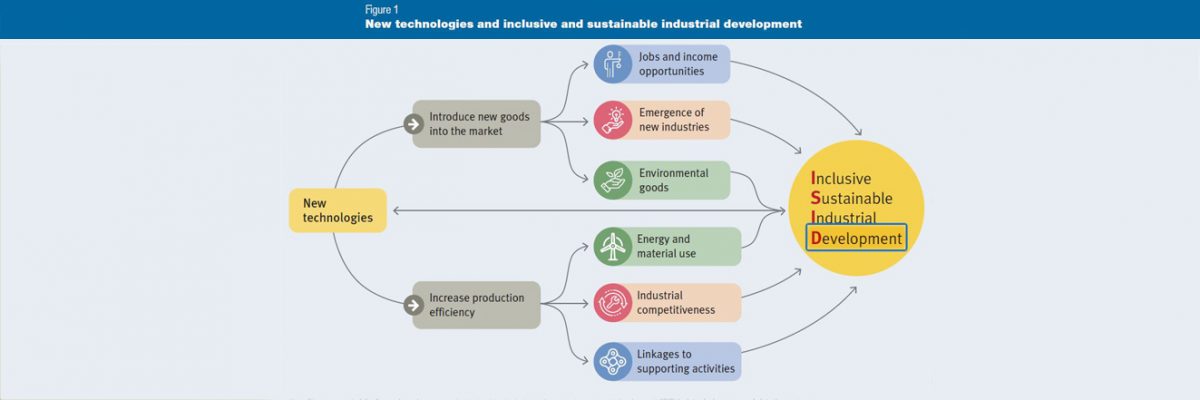
Utilizing Technology and Mass Production
A contribution of advanced technologies to the mass production sector will decrease need for materials and energy. Less need for raw material during production will allow natural resources to be used in a responsible manner. Efficient use of materials will also help us reduce our current annual carbon footprint of 85.9 billion tons. Furthermore, as robotic factory systems get smarter in the future coordinated work will speed up the production process. Likewise production mistakes and energy consumption required per product will decrease.
Perhaps the most important effect of less material and energy use will be the reduced cost and sales prices. In addition to the decreasing material and energy use per item, technological developments will minimize need of human labor. Minimal use of human labor will further reduce production costs. Decreasing product prices will play major role in overcoming extreme poverty as it increases product availability. Marginalized populations will see an increase in their quality of life due to cheap and ethically produced items which offer solutions to their daily problems.
Other advantages of advanced production will be increasing socio-economic level of employees, increasing monthly income and decreasing heavy workload. In the future, advanced production technologies will allow machine to execute heavy work. Factory workers will only maintain and program the technologies that do the heavy work. Blue-collar employees who work as technology monitors will be more educated and earn a better income because they specialize in working with advanced technologies.
 Primitive Use of Artificial Intelligence: A Look from Past to Present
Primitive Use of Artificial Intelligence: A Look from Past to Present  The Future of Medical Design
The Future of Medical Design  A Night Full of Prizes: Celebrating 4 Wins at iF Design Awards 2023
A Night Full of Prizes: Celebrating 4 Wins at iF Design Awards 2023